Difference between revisions of "HMS Demo"
From ArmadeusWiki
(→FPGA structure) |
m (→FPGA structure) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
[[image:fpga_struct.png|center|700px|thumb|'''figure 2''' - ''FPGA internal structure'']] | [[image:fpga_struct.png|center|700px|thumb|'''figure 2''' - ''FPGA internal structure'']] | ||
| − | Components are included in FPGA using [POD] to ease integration : | + | Components are included in FPGA using [[POD]] to ease integration : |
* input : Read input value using a serial bus like SPI. This component can generate an interrupt on input change. | * input : Read input value using a serial bus like SPI. This component can generate an interrupt on input change. | ||
Revision as of 10:24, 25 June 2009
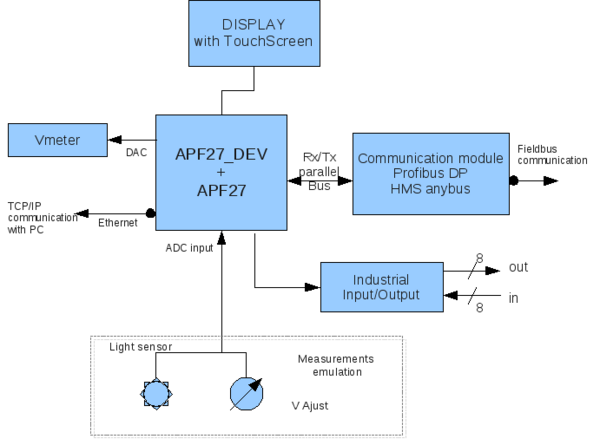
HMS demo board is an electronic development board that demonstrates industrial capabilities of the APF27 ARMadeus board.
This article will describe the structure of the board.
Hardware structure
This board includes :
- An Anybus[1] CompactCom adaptator from HMS.
- 8 industrial inputs using SN65HVS882 chip
- 8 industrial outputs with simple shift register
- a LCD screen
- Voltage needles
- Light sensor
- Potentiometer button
- and all APF27Dev capabilities
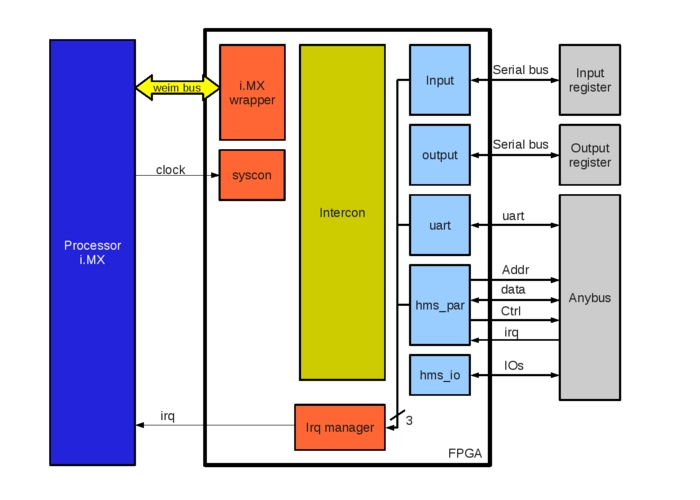
FPGA structure
The structure of the FPGA is represented bellow. All modules are connected on i.MX wrapper with the wishbone bus (16 bits data), the intercon is used to decode addresses.
Components are included in FPGA using POD to ease integration :
- input : Read input value using a serial bus like SPI. This component can generate an interrupt on input change.
- output: Write output value using a serial bus like SPI.
- uart : Anybus CompactCom can be drove using a simple uart TTL bus.
- hms_par: For more complex design, Anybus CompactCom can use a «parallel bus» like memory bus.
- hms_io : Anybus has some IO for status and configuration, this component is used to configure it.
Software structure
Links
Notes
- ↑ Anybus is a registered trademark of HMS Industrial Networks AB, Sweden, USA, Germany and other countries.