Difference between revisions of "APF27 FPGA-IMX interface description"
m |
m (Brushed up) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
This article describe the interface between IMX and Spartan3A on APF27. | This article describe the interface between IMX and Spartan3A on APF27. | ||
| − | Documentation of i.MX interface can be found in | + | Documentation of i.MX interface can be found in the iMX reference manual, chapter 17, |
«Wireless External Interface Module ('''WEIM''')». | «Wireless External Interface Module ('''WEIM''')». | ||
== Hardware == | == Hardware == | ||
| − | + | The detailled electronic schematics of apf27 fpga interface can be found on | |
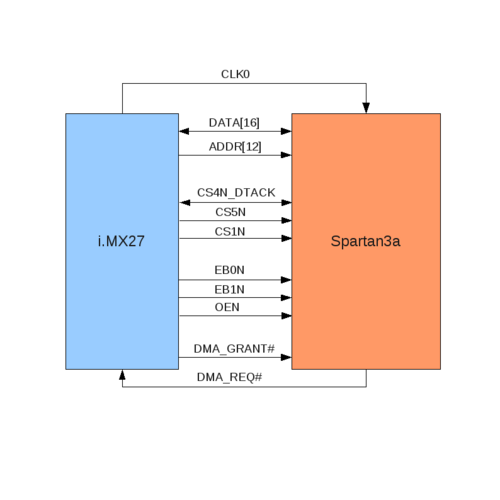
| − | [http://www.armadeus.com/_downloads/apf27/hardware/apf27_V1.2.pdf this document] page 11. | + | [http://www.armadeus.com/_downloads/apf27/hardware/apf27_V1.2.pdf this document] page 11. A simplified schema is shown below on figure 1. |
[[image:fpgaimx_wire.png|center|500px|thumb|'''figure 1''' - ''FPGA-i.MXL wiring'']] | [[image:fpgaimx_wire.png|center|500px|thumb|'''figure 1''' - ''FPGA-i.MXL wiring'']] | ||
| − | + | The signals used in the design are: | |
| − | * '''CLKO''' : Clock generated by i.MX | + | * '''CLKO''': Clock generated by i.MX. Used as general clock by the FPGA. |
| − | * '''DATA[16]''' : 16 bits data bus. | + | * '''DATA[16]''': 16 bits data bus. |
| − | * '''ADDR[13]''' : 12 bits | + | * '''ADDR[13]''': 12 bits address bus, least significant bit (ADDR[0]) is not used because only word access are done. |
* '''CS4N_DTACK''': '''C'''hip '''S'''elect 4 or '''D'''ata '''T'''ransmit '''ACK'''nowledge. | * '''CS4N_DTACK''': '''C'''hip '''S'''elect 4 or '''D'''ata '''T'''ransmit '''ACK'''nowledge. | ||
| − | * '''CS5''','''CS1''' : '''C'''hip '''S'''elect 5 and 1. | + | * '''CS5''','''CS1''': '''C'''hip '''S'''elect 5 and 1. |
* '''EB0N''' and '''EB1N''': For '''E'''nable '''B'''yte, write signal for lower byte and upper byte on data bus. | * '''EB0N''' and '''EB1N''': For '''E'''nable '''B'''yte, write signal for lower byte and upper byte on data bus. | ||
| − | * '''OEN''' : For '''O'''utput '''E'''nable bit, read signal. | + | * '''OEN''': For '''O'''utput '''E'''nable bit, read signal. |
| − | * '''DMA_GRANT#''' and '''DMA_REQ#''' : Signals to use DMA on i.MX. | + | * '''DMA_GRANT#''' and '''DMA_REQ#''': Signals to use DMA on i.MX. |
| − | Each chip select has its own configuration that can be | + | Each chip select has its own configuration (timing, address range, ...) that can be used for different slaves in the FPGA. |
| − | + | ||
| − | '''CLKO''' is configured at 133MHz to be synchronous with '''WEIM''' bus that | + | '''CLKO''' is by default configured to run at 133MHz to be synchronous with the '''WEIM''' bus that is internally clocked at 133MHz, too. |
| − | is internally clocked at 133MHz too. | + | |
== Chip Select Timings configuration == | == Chip Select Timings configuration == | ||
===Present configuration (static timing)=== | ===Present configuration (static timing)=== | ||
| − | + | The default configuration uses '''CS5''' for accessing the FPGA. 32 bits register CS5 | |
is used to configure all timing for this chip select. It's default | is used to configure all timing for this chip select. It's default | ||
| − | configuration is : | + | configuration is: |
| − | * CS5U (Upper 16bits,see page 521 of reference manual ) : mw D8002050 00000600 | + | * CS5U (Upper 16bits, see page 521 of reference manual ): mw D8002050 00000600 |
| − | This will add 6 waits state on access to read value correctly (WSC : Wait | + | This will add 6 waits state on access to read value correctly (WSC: Wait |
State Control). | State Control). | ||
| − | * CS5L (Lower 16bits,see page 525 of reference manual) : mw D8002054 00000D01 | + | * CS5L (Lower 16bits,see page 525 of reference manual): mw D8002054 00000D01 |
Enable chip select (CSEN), Enable for only write access EB[] (EBC) and select data port size to | Enable chip select (CSEN), Enable for only write access EB[] (EBC) and select data port size to | ||
| − | 16bits (DSZ : Data port SiZe). | + | 16bits (DSZ: Data port SiZe). |
| − | * CS5A (additionnal register, page 528) : mw D8002058 0 | + | * CS5A (additionnal register, page 528): mw D8002058 0 |
| − | * WCR (WEIM Configuration Register) : mw D8002060 00002000 | + | * WCR (WEIM Configuration Register): mw D8002060 00002000 |
Address unshifted for CS5 (AUS5) | Address unshifted for CS5 (AUS5) | ||
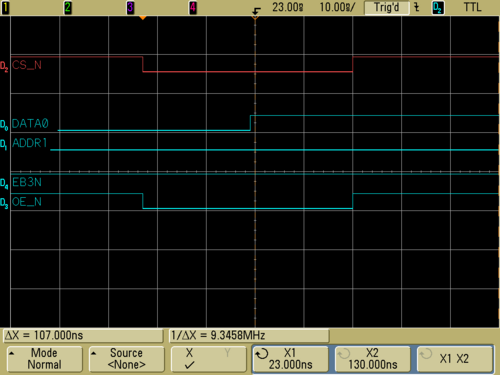
[[image:timingstatic.png|center|500px|thumb|'''figure 2''' - ''Static timings chronograms'']] | [[image:timingstatic.png|center|500px|thumb|'''figure 2''' - ''Static timings chronograms'']] | ||
| − | With this configuration, | + | With this configuration, the access time (read/write) to the FPGA is set to 50ns. |
This configuration is interesting because all timings are under control. But | This configuration is interesting because all timings are under control. But | ||
| − | the problem is that to be perfectly synchronous, | + | the problem is that to be perfectly synchronous, the FPGA is clocked at 133MHz |
like WEIM and some IP design doesn't work at this frequency. | like WEIM and some IP design doesn't work at this frequency. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Alternative configuration (with DTACK)=== |
| − | To solve | + | To solve the problem, another solution can be the DTACK signal (asynchronous protocol). The DTACK signal |
| − | is emmited by slave to master when write/read is done. | + | is emmited by the slave to master when write/read is done. |
| − | With this solution, access time is variable and | + | With this solution, access time is variable and the timing is not static any more. |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Timing register configuration=== | ||
| − | + | All register configurations for external memory are done in u-boot. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | All | + | |
Configuration file can be found in | Configuration file can be found in | ||
''buildroot/project_build_armv5te/<project_name>/u-boot-1.3.4/include/configs/apf27.h'' | ''buildroot/project_build_armv5te/<project_name>/u-boot-1.3.4/include/configs/apf27.h'' | ||
And is saved in armadeus tree at | And is saved in armadeus tree at | ||
''buildroot/target/device/armadeus/apf27/apf27.h | ''buildroot/target/device/armadeus/apf27/apf27.h | ||
Revision as of 10:45, 5 August 2009
This article describe the interface between IMX and Spartan3A on APF27. Documentation of i.MX interface can be found in the iMX reference manual, chapter 17, «Wireless External Interface Module (WEIM)».
Contents
Hardware
The detailled electronic schematics of apf27 fpga interface can be found on this document page 11. A simplified schema is shown below on figure 1.
The signals used in the design are:
- CLKO: Clock generated by i.MX. Used as general clock by the FPGA.
- DATA[16]: 16 bits data bus.
- ADDR[13]: 12 bits address bus, least significant bit (ADDR[0]) is not used because only word access are done.
- CS4N_DTACK: Chip Select 4 or Data Transmit ACKnowledge.
- CS5,CS1: Chip Select 5 and 1.
- EB0N and EB1N: For Enable Byte, write signal for lower byte and upper byte on data bus.
- OEN: For Output Enable bit, read signal.
- DMA_GRANT# and DMA_REQ#: Signals to use DMA on i.MX.
Each chip select has its own configuration (timing, address range, ...) that can be used for different slaves in the FPGA.
CLKO is by default configured to run at 133MHz to be synchronous with the WEIM bus that is internally clocked at 133MHz, too.
Chip Select Timings configuration
Present configuration (static timing)
The default configuration uses CS5 for accessing the FPGA. 32 bits register CS5 is used to configure all timing for this chip select. It's default configuration is:
- CS5U (Upper 16bits, see page 521 of reference manual ): mw D8002050 00000600
This will add 6 waits state on access to read value correctly (WSC: Wait State Control).
- CS5L (Lower 16bits,see page 525 of reference manual): mw D8002054 00000D01
Enable chip select (CSEN), Enable for only write access EB[] (EBC) and select data port size to 16bits (DSZ: Data port SiZe).
- CS5A (additionnal register, page 528): mw D8002058 0
- WCR (WEIM Configuration Register): mw D8002060 00002000
Address unshifted for CS5 (AUS5)
With this configuration, the access time (read/write) to the FPGA is set to 50ns.
This configuration is interesting because all timings are under control. But the problem is that to be perfectly synchronous, the FPGA is clocked at 133MHz like WEIM and some IP design doesn't work at this frequency.
Alternative configuration (with DTACK)
To solve the problem, another solution can be the DTACK signal (asynchronous protocol). The DTACK signal is emmited by the slave to master when write/read is done. With this solution, access time is variable and the timing is not static any more.
Timing register configuration
All register configurations for external memory are done in u-boot. Configuration file can be found in buildroot/project_build_armv5te/<project_name>/u-boot-1.3.4/include/configs/apf27.h And is saved in armadeus tree at buildroot/target/device/armadeus/apf27/apf27.h