Difference between revisions of "How to make a VHDL design in Ubuntu/Debian"
(→Making a simple project) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category: FPGA]] | ||
| + | |||
This tutorial describes how to install all the necessary tools to develop simple designs under Ubuntu for the Armadeus Project.<br> | This tutorial describes how to install all the necessary tools to develop simple designs under Ubuntu for the Armadeus Project.<br> | ||
As Ubuntu is a Debian based distribution, all the informations on this page should work with Debian too. | As Ubuntu is a Debian based distribution, all the informations on this page should work with Debian too. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
== Making a simple project == | == Making a simple project == | ||
| − | It's a good idea to make a | + | It's a good idea to make a clean project tree for your design, because different software are |
used and each generates a large amount of files. | used and each generates a large amount of files. | ||
| Line 22: | Line 24: | ||
== Simulation == | == Simulation == | ||
| − | To stay in the | + | To stay in the Free Software spirit, the best method to simulate is to use [http://ghdl.free.fr/ GHDL] (based on GCC).<br> |
| − | + | To install it on Ubuntu you just have to type : | |
| − | sudo apt-get install ghdl | + | $ sudo apt-get install ghdl |
| − | You can find a good tutorial for using | + | You can find a good tutorial for using GHDL [http://forum.ubuntu-fr.org/viewtopic.php?pid=1545563#p839075 here] and on [http://ghdl.free.fr/ghdl/Starting-with-GHDL.html#Starting-with-GHDL the official website]. It's supposed that the project tree |
| − | used is this one | + | used is this one described previously. |
Analysing files: | Analysing files: | ||
| − | ghdl -i --ieee=synopsys --warn-no-vital-generic --workdir=simu --work=work src/*.vhdl testbench/testb_file.vhd | + | $ ghdl -i --ieee=synopsys --warn-no-vital-generic --workdir=simu --work=work src/*.vhdl testbench/testb_file.vhd |
And compile: | And compile: | ||
| − | ghdl -m --ieee=synopsys --warn-no-vital-generic --workdir=simu --work=work testb_file | + | $ ghdl -m --ieee=synopsys --warn-no-vital-generic --workdir=simu --work=work testb_file |
| + | After that a binary file named ''testb_file'' is created; to launch simulation we just have to: | ||
| + | $ ./testb_file --stop-time=500ns --vcdgz=testb_file.vcdgz | ||
| + | The stop time option sets the simulation time and the vcdgz option will generate a gunzip compressed wave file to visualize the result. | ||
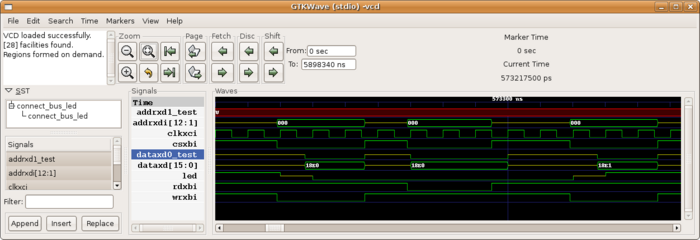
| − | + | Visualizing the result can be done with gtkwave: | |
| − | + | $ sudo apt-get install gtkwave | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | sudo apt-get install gtkwave | + | |
We can launch it with the following command : | We can launch it with the following command : | ||
| − | gunzip --stdout testb_file.vcdgz | gtkwave --vcd | + | $ gunzip --stdout testb_file.vcdgz | gtkwave --vcd |
[[Image:gtkwave.png|700px]] | [[Image:gtkwave.png|700px]] | ||
| − | It can be a good idea to | + | It can be a good idea to make a Makefile instead of typing all this commands, here is a little Makefile: |
<code lang="makefile"> | <code lang="makefile"> | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
VIEW_CMD = /usr/bin/gtkwave | VIEW_CMD = /usr/bin/gtkwave | ||
| − | ghdl- | + | ghdl-compile : |
mkdir -p simu | mkdir -p simu | ||
$(GHDL_CMD) -i $(GHDL_FLAGS) --workdir=simu --work=work $(SIMFILES) $(FILES) | $(GHDL_CMD) -i $(GHDL_FLAGS) --workdir=simu --work=work $(SIMFILES) $(FILES) | ||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
to use it, just write : | to use it, just write : | ||
| − | make ghdl-compile | + | $ make ghdl-compile |
| − | to compile | + | to compile, then: |
| − | make ghdl-run | + | $ make ghdl-run |
| − | to run the design | + | to run the design, then: |
| − | make ghdl-view | + | $ make ghdl-view |
| − | to launch gtkwave and visualize results | + | to launch gtkwave and visualize the results. |
== Syntesis, place & route == | == Syntesis, place & route == | ||
=== GUI installation === | === GUI installation === | ||
| − | To synthesize the design it is mandatory to use Xilinx tools (It's not exactly true, others tools can be used for synthesize like Mentor tools, but at the end to make the bitstream Xilinx tools are | + | To synthesize the design it is mandatory to use Xilinx tools (It's not exactly true, others tools can be used for synthesize like Mentor tools, but at the end, to make the bitstream, Xilinx tools are mandatory), fortunately Xilinx provides his webpack for Linux. [[ISE_WebPack_installation_on_Linux| Click here if you didn't install it yet.]] |
| − | + | To launch the floorplanner, DISPLAY has to be change: | |
| − | + | <pre class="host"> | |
| + | export DISPLAY=:0 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | After this installation, ISE can be found in the directory ''$(Xilinx_root_dir)/bin/lin''. | |
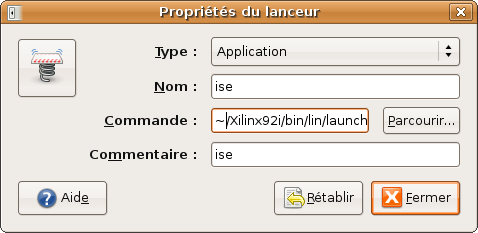
| − | + | To avoid retyping export, a little script ''launch_ise.sh'' can be made in ''bin/lin/'' directory: | |
| + | <source lang="bash"> | ||
| + | #!/bin/bash | ||
| + | export DISPLAY=:0 | ||
| + | ~/Xilinx92i/bin/lin/ise | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Then make launch click : | Then make launch click : | ||
| Line 121: | Line 120: | ||
There is a good tutorial on [http://harded.free.fr/site/?p=31 harded.free.fr]. | There is a good tutorial on [http://harded.free.fr/site/?p=31 harded.free.fr]. | ||
| − | === Using Xilinx | + | === Using Xilinx command line tools for shell syntesis === |
See [http://panteltje.com/panteltje/fpga/index.html Using Xilinx Webpack-8.1i on grml Linux in scripted mode, without GUI] for an introduction. | See [http://panteltje.com/panteltje/fpga/index.html Using Xilinx Webpack-8.1i on grml Linux in scripted mode, without GUI] for an introduction. | ||
| Line 132: | Line 131: | ||
ldconfig | ldconfig | ||
| − | Then modify your .bashrc | + | Then modify your .bashrc (add at the end): |
PLATFORM=lin | PLATFORM=lin | ||
XILINX=Xilinx_directory | XILINX=Xilinx_directory | ||
| Line 139: | Line 138: | ||
export PATH | export PATH | ||
| − | Then | + | Then ISE can be used in command line (xst, ngdbuild, map, bit,...). To avoid typing very long commands it can be a good idea to use a Makefile, xess.com provide a full [http://www.xess.com/appnotes/makefile.php Makefile] to do this and a basic Makefile for simulation and synthesis can be found in the armadeus gitlab project: [https://gitlab.com/armadeus/armadeus-bsp/-/blob/master/firmware/wishbone_example/wishbone_example9328_27/Makefile]. To use it modify the head and write the names of your files : |
| + | *General options | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
# project name | # project name | ||
PROJECT=bus_led_top | PROJECT=bus_led_top | ||
# vhdl files | # vhdl files | ||
FILES = src/bus_led.vhd src/bus_led_top.vhd | FILES = src/bus_led.vhd src/bus_led_top.vhd | ||
| + | |||
| + | * constraints for synthesis | ||
| + | |||
# pin configuration | # pin configuration | ||
UCF_FILE = src/bus_led.ucf | UCF_FILE = src/bus_led.ucf | ||
# Synthesis constraints file | # Synthesis constraints file | ||
XCF_FILE = | XCF_FILE = | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Testbench options | ||
| + | |||
# testbench | # testbench | ||
SIMTOP = led_top_tb | SIMTOP = led_top_tb | ||
SIMFILES = ../apf_pkg/apf_test_pkg.vhd testbench/led_top_tb.vhd | SIMFILES = ../apf_pkg/apf_test_pkg.vhd testbench/led_top_tb.vhd | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Simulation can stop after a given time or after an assert error (end of test for example) | ||
| + | |||
# Simu break condition | # Simu break condition | ||
GHDL_SIM_OPT = --assert-level=error | GHDL_SIM_OPT = --assert-level=error | ||
#GHDL_SIM_OPT = --stop-time=500ns | #GHDL_SIM_OPT = --stop-time=500ns | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 12:44, 30 June 2022
This tutorial describes how to install all the necessary tools to develop simple designs under Ubuntu for the Armadeus Project.
As Ubuntu is a Debian based distribution, all the informations on this page should work with Debian too.
Contents
Editing VHDL
To edit VHDL code all standard editing softwares like Vim, Emacs or others can be used. But Emacs has a really good vhdl-mode used by lots of designers. If you hate Emacs, you can use the xilinx-embedded editor or vim with a VHDL-plugin under development.
Making a simple project
It's a good idea to make a clean project tree for your design, because different software are used and each generates a large amount of files.
Here is an example of a VHDL project tree :
- MySimple_project/
- src/ for all sources files (.vhd,.ucf,.xcf)
- testbench/ VHDL sources files for testing your design
- ise/ Xilinx web pack will work in this directory
- simu/ All files generated by the simulator
Simulation
To stay in the Free Software spirit, the best method to simulate is to use GHDL (based on GCC).
To install it on Ubuntu you just have to type :
$ sudo apt-get install ghdl
You can find a good tutorial for using GHDL here and on the official website. It's supposed that the project tree used is this one described previously.
Analysing files:
$ ghdl -i --ieee=synopsys --warn-no-vital-generic --workdir=simu --work=work src/*.vhdl testbench/testb_file.vhd
And compile:
$ ghdl -m --ieee=synopsys --warn-no-vital-generic --workdir=simu --work=work testb_file
After that a binary file named testb_file is created; to launch simulation we just have to:
$ ./testb_file --stop-time=500ns --vcdgz=testb_file.vcdgz
The stop time option sets the simulation time and the vcdgz option will generate a gunzip compressed wave file to visualize the result.
Visualizing the result can be done with gtkwave:
$ sudo apt-get install gtkwave
We can launch it with the following command :
$ gunzip --stdout testb_file.vcdgz | gtkwave --vcd
It can be a good idea to make a Makefile instead of typing all this commands, here is a little Makefile:
# project name
PROJECT=bus_led_top
# vhdl files
FILES = src/bus_led.vhd src/bus_led_top.vhd
# testbench
SIMTOP = led_top_tb
SIMFILES = testbench/led_top_tb.vhd
# Simu break condition
GHDL_SIM_OPT = --assert-level=error
#GHDL_SIM_OPT = --stop-time=500ns
SIMDIR = simu
SYNTHFILES = bin/bus_led_ise/netgen/synthesis
GHDL_CMD = ghdl
GHDL_FLAGS = --ieee=synopsys --warn-no-vital-generic
VIEW_CMD = /usr/bin/gtkwave
ghdl-compile :
mkdir -p simu
$(GHDL_CMD) -i $(GHDL_FLAGS) --workdir=simu --work=work $(SIMFILES) $(FILES)
$(GHDL_CMD) -m $(GHDL_FLAGS) --workdir=simu --work=work $(SIMTOP)
@mv $(SIMTOP) simu/$(SIMTOP)
ghdl-run :
@$(SIMDIR)/$(SIMTOP) $(GHDL_SIM_OPT) --vcdgz=$(SIMDIR)/$(SIMTOP).vcdgz
ghdl-view:
gunzip --stdout $(SIMDIR)/$(SIMTOP).vcdgz | $(VIEW_CMD) --vcd
ghdl-clean :
$(GHDL_CMD) --clean --workdir=simu
to use it, just write :
$ make ghdl-compile
to compile, then:
$ make ghdl-run
to run the design, then:
$ make ghdl-view
to launch gtkwave and visualize the results.
Syntesis, place & route
GUI installation
To synthesize the design it is mandatory to use Xilinx tools (It's not exactly true, others tools can be used for synthesize like Mentor tools, but at the end, to make the bitstream, Xilinx tools are mandatory), fortunately Xilinx provides his webpack for Linux. Click here if you didn't install it yet.
To launch the floorplanner, DISPLAY has to be change:
export DISPLAY=:0
After this installation, ISE can be found in the directory $(Xilinx_root_dir)/bin/lin. To avoid retyping export, a little script launch_ise.sh can be made in bin/lin/ directory:
#!/bin/bash
export DISPLAY=:0
~/Xilinx92i/bin/lin/ise
Then make launch click :
There is a good tutorial on harded.free.fr.
Using Xilinx command line tools for shell syntesis
See Using Xilinx Webpack-8.1i on grml Linux in scripted mode, without GUI for an introduction.
First of all, library files has to be copied in library directory :
sudo -s mkdir /usr/local/lib/xilinx/ cp Xilinx_directory/bin/lin/*.so /usr/local/lib/xilinx/ echo /usr/local/lib/xilinx >> /etc/ld.so.conf ldconfig
Then modify your .bashrc (add at the end):
PLATFORM=lin XILINX=Xilinx_directory export XILINX PATH=Xilinx_directory/bin/lin:$PATH export PATH
Then ISE can be used in command line (xst, ngdbuild, map, bit,...). To avoid typing very long commands it can be a good idea to use a Makefile, xess.com provide a full Makefile to do this and a basic Makefile for simulation and synthesis can be found in the armadeus gitlab project: [1]. To use it modify the head and write the names of your files :
- General options
# project name PROJECT=bus_led_top # vhdl files FILES = src/bus_led.vhd src/bus_led_top.vhd
- constraints for synthesis
# pin configuration UCF_FILE = src/bus_led.ucf # Synthesis constraints file XCF_FILE =
- Testbench options
# testbench SIMTOP = led_top_tb SIMFILES = ../apf_pkg/apf_test_pkg.vhd testbench/led_top_tb.vhd
- Simulation can stop after a given time or after an assert error (end of test for example)
# Simu break condition GHDL_SIM_OPT = --assert-level=error #GHDL_SIM_OPT = --stop-time=500ns